
Today’s world is digital-first. Transactions can be done online, but it can be hard to verify the legitimacy of the parties involved. Businesses must find a way to verify their customers’ identities. However, customers also want to be sure that their information will be secure when they hand it over online.
Authentication and verification appeared as solutions for this problem. In online platforms where users need to store sensitive information, like legit online casino platforms, users would usually be able to find both features. They’ll get to choose an authentication method that secures their account while undergoing identity verification when making transactions.
So, why does digital identity verification matter in this digital world? As a user, it’s crucial to understand how to protect yourself while online, so let’s learn further about it.
How Digital Identity Verification Works
Digital identity verification is a multi-layered process that includes data sources, biometrics, and document analysis. The process starts with a document verification. Users would be asked to upload a few documents that can prove their identity. This can be a driver’s license, a national ID, or a passport.
Once uploaded, the AI models will analyze each document by their fonts, holographic patterns, and textures. Biometric verification is the next step, where the verification process ensures that the documents uploaded genuinely belong to the user. It also has facial recognition to confirm that the user is present and that they’re not detecting pictures, videos, or deepfakes.
The whole digital identity verification process’s main aim is to avoid fraudsters. However, it’s also a way to ensure the verification process isn’t complicating legitimate users. Most users won’t notice some of the steps as they’re done behind the screen. The system will only flag suspicious activities that won’t bother legitimate users.
Use Cases
Authentication and verification have been widely used across industries for a long time. Some of the common examples include:
- Financial services: Fintechs and banks rely heavily on identity verification. It’s crucial, especially for transactions like loan approvals, account openings, and cross-border payments. Mobile financial services, such as mobile banking, often depend on biometric verification.
- Healthcare: Healthcare usually implements identity verification as one way for them to safeguard their patient records. The aim is to expedite insurance claims and prevent prescription fraud.
- E-commerce and retail: As online retailers often require users to transact digitally, account creation and high-value purchases usually require identification verification.
Benefits of Digital Identity Verification
Identity verification doesn’t only work to improve security. It can benefit a business and users alike in many ways, including:
- Enhancing security: Security is still the main function of identity verification. However, today’s technologies can detect deepfakes and digital manipulation more effectively than traditional methods.
- Operational efficiency: As digital identity verification is done automatically. Therefore, it reduces manual workloads that would take longer and be less efficient.
- Customer experience: Mobile-first verification can now make identity verifications easier and faster to do.
- Compliance readiness: Organizations need to comply with various regulations, such as AML (Anti-Money Laundering) and KYC (Know Your Customers), which require verification.
How Authentication Works
Authentication is one of the methods users can use to verify their identity. The most common authentication examples would be passwords. They’re unique to each user, so a password is the common way people have been doing it for years to authenticate their accounts. As technology becomes more advanced, users can now authenticate using biometric data, which is more secure than a password.
Another common authentication method is SMS OTP code. The platform would send a one-time use unique code to the user’s registered phone number. Only when the user inputs the one-time code would they be able to sign in.
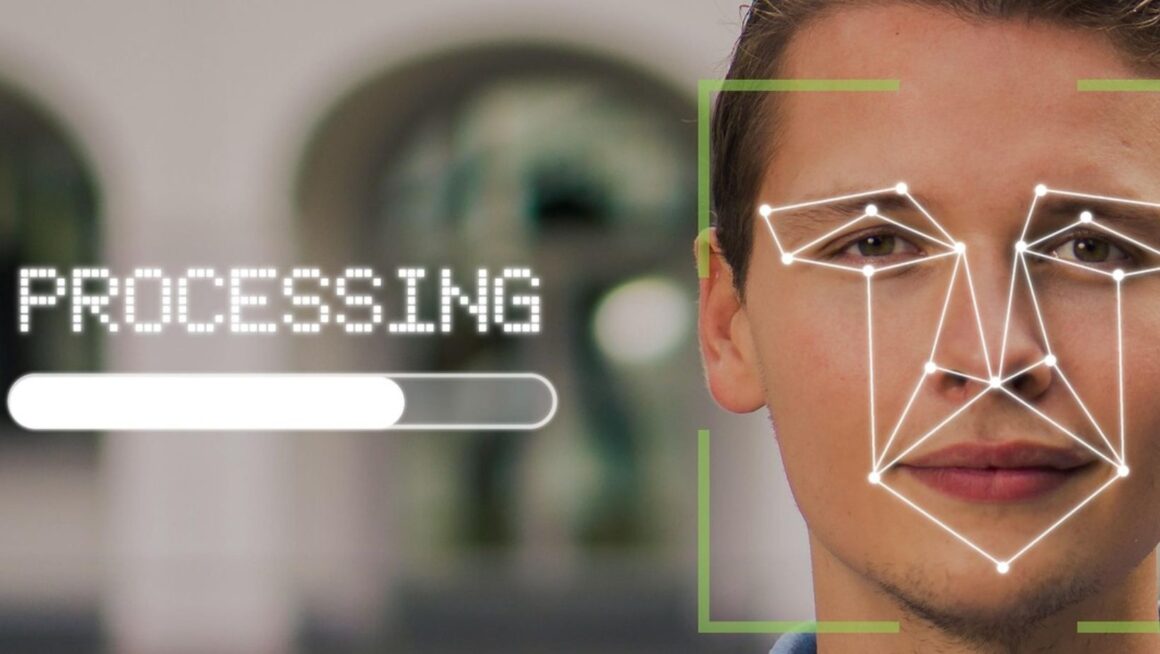
Authentication is a process that happens repeatedly. It’ll happen on every access attempt made to a protected system. However, the process has now become seamless enough that it doesn’t feel like a hassle to users, but just a part of the login process.
There are three core categories of authentication. When asked to authenticate, users would usually be asked to provide either:
- Something they know: It can be a PIN, an answer to a previously set security question, or their account’s password.
- Something they have: This can be an OTP, an authenticator app, or a hardware token.
- Biometric data: Most devices can now recognize fingerprints or have facial recognition technology. It’s considered the most secure authentication form.
Some platforms allow users to activate more than one authentication method. For services or platforms needing higher security measures, they usually provide multifactor authentication for stronger protection against unauthorized access.
Why Authentication Matters
Cybersecurity in this era is a high priority for all digital platforms. Not only does it protect the users, but it can also be a safety feature that contributes to the business. It’s a powerful defense that businesses with a digital presence should have in today’s world. Authentication alone can help protect a platform against:
- Financial loss: Recovering from a data breach can be highly costly for any business.
- Reputation damage: Although a platform has managed to protect its customers for years, one breach can quickly break customers’ trust in the entire brand.
- Legal trouble: Being unable to protect a customer can result in a lawsuit or being taken as a non-compliance act with regulatory bodies like PSD2, CCPA, or GDPR.
- Lack of appeal: Modern users are very aware of cyberthreats and digital security. Security-conscious users would often disregard businesses that can’t showcase their security features.












